
As a result, the retention ratio helps investors determine a company’s reinvestment rate. However, companies that hoard too much profit might not be using their cash effectively and might be better off had the money been invested in new equipment, technology, or expanding product lines. New companies typically don’t pay dividends since they’re still growing and need the capital to finance growth. However, established companies usually pay a portion of their retained earnings out as dividends while also reinvesting a portion back into the company. In financial modeling, it’s necessary to have a separate schedule for modeling retained earnings.
- Revenue is the money generated by a company during a period but before operating expenses and overhead costs are deducted.
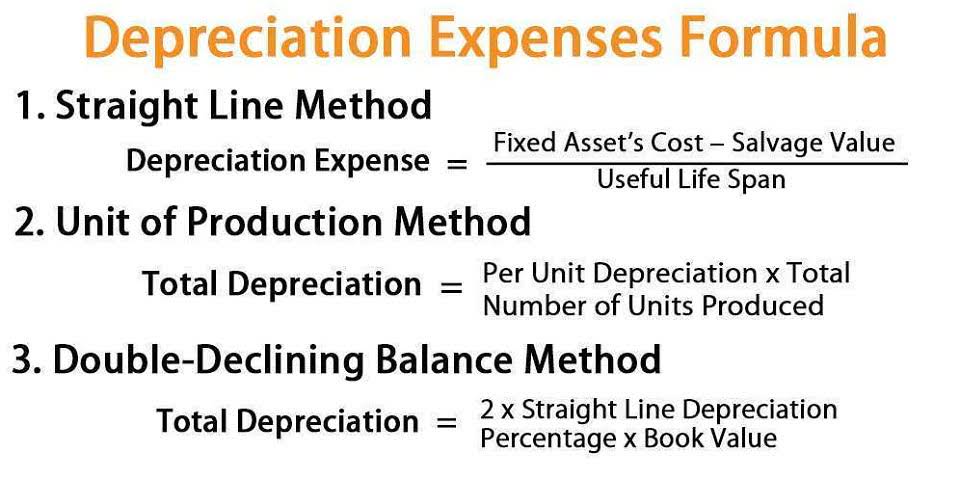
- Examples of these items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and other operating expenses.
- It is prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
- But, you can also record retained earnings on a separate financial statement known as the statement of retained earnings.
- Those account balances are then transferred to the Retained Earnings account.
- Retained earnings is the cumulative amount of earnings since the corporation was formed minus the cumulative amount of dividends that were declared.
Example of retained earnings statement with cash dividends paid
Retained earnings are calculated through taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding to the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts. In the next accounting cycle, the RE ending balance from the previous accounting period will now become the retained earnings beginning balance. The figure is calculated at the end of each accounting period (monthly/quarterly/annually). As the formula suggests, retained earnings are dependent on the corresponding figure of the previous term.
How to Calculate the Effect of a Cash Dividend on Retained Earnings?
Higher retained earnings may be a sign of a company’s financial strength as it saves up funds to expand—or it could be a missed opportunity for paying dividends. The business retained earnings balance of the previous year is the opening balance of the current year. As a key indicator of a company’s financial performance over time, retained earnings are important to investors in gauging a company’s financial health. This post will walk step by step through what retained earnings are, their importance, and provide an example. Net sales are calculated as gross revenues net of discounts, returns, and allowances.

Find your beginning retained earnings balance
Such a balance can be both positive or negative, depending on the net profit or losses made by the company over the years and the amount of dividend paid. The beginning period retained earnings is nothing but the previous year’s retained earnings, as appearing in the previous year’s balance sheet. The company’s retained earnings calculation is laid out nicely in its consolidated retained earning credit or debit statements of shareowners’ equity statement. Here we can see the beginning balance of its retained earnings (shown as reinvested earnings), the net income for the period, and the dividends distributed to shareholders in the period. A company’s equity reflects the value of the business, and the retained earnings balance is an important account within equity.
Statement of retained earnings example
To see how retained earnings impact shareholders’ equity, let’s look at an example. Instead, they reallocate a portion of the RE to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts. This allocation does not impact the overall size of the company’s balance sheet, but it does decrease the value of stocks per share. Retained Earnings (RE) are the accumulated portion of a business’s profits that are not distributed as dividends to shareholders but instead are reserved for reinvestment back into the business.

Thus, if the company had a market value of $2 million before the stock dividend declaration, it’s market value still is $2 million after the stock dividend is declared. This is because due to the increase in the number of shares, dilution of the shareholding takes place, which reduces the book value per share. And this reduction in book value per share reduces the market price of the share accordingly. These are the long term investors who seek periodic payments in the form of dividends as a return on the money invested by them in your company.
At the end of an accounting year, the balances in a corporation’s revenue, gain, expense, and loss accounts are used to compute the year’s net income. Those account balances are then transferred to the Retained Earnings account. When the year’s revenues and gains exceed the expenses and losses, the corporation will have a positive net income which causes the balance in the Retained Earnings account to increase. The next step is to add the net income (or net loss) for the current accounting period. The net income is obtained from the company’s income statement, which is prepared first before the statement of retained earnings. If you see your beginning retained earnings as negative, that could mean that the current accounting cycle you’re in has a larger net loss than your beginning balance of retained earnings.
What do Retained Earnings tell You?
Unappropriated retained earnings have not been earmarked for anything in particular. They are generally available for distribution as dividends or reinvestment in the business. Retained earnings is the cumulative amount of earnings since the corporation was formed minus the cumulative amount of dividends that were declared. Retained earnings is the corporation’s past earnings that have not been distributed as dividends to its stockholders. If you have a net loss and low or negative beginning retained earnings, you can have negative retained earnings.

For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
- Traders who look for short-term gains may also prefer dividend payments that offer instant gains.
- This is the retained earnings amount from the end of the previous financial period.
- Thus, retained earnings are the profits of your business that remain after the dividend payments have been made to the shareholders since its inception.
- Cash dividends result in an outflow of cash and are paid on a per-share basis.
- In addition to considering revenue, it is impacted by the company’s cost of goods sold, operating expenses, taxes, interest, depreciation, and other costs.
- This line item reports the net value of the company—how much your company is worth if you decide to liquidate all your assets.
